
Conveying Meaning: The Art of Effective Communication
How do we truly master the art of conveying meaning in our increasingly complex communication landscape? The ability to convey meaning effectively has become one of the most critical skills in our interconnected world, where misunderstandings can have far-reaching consequences and clear communication can open doors to unprecedented opportunities. Understanding the nuances of conveying meaning through various channels—from verbal and written communication to visual symbols and digital platforms—is essential for personal success, professional advancement, and meaningful human connection.
In this comprehensive exploration of conveying meaning, we'll delve deep into the sophisticated mechanisms that enable us to share ideas, emotions, and complex concepts across diverse audiences, cultural boundaries, and communication mediums.
Maybe you may be interestedThe Essence of Courtesy: Unveiling its True Meaning- The Fundamental Science of Conveying Meaning: Cognitive and Linguistic Foundations
- Multi-Modal Approaches to Conveying Meaning: Beyond Verbal Communication
- Digital Age Strategies for Conveying Meaning: Technology-Enhanced Communication
- Cross-Cultural Mastery in Conveying Meaning: Global Communication Excellence
- Industry-Specific Applications of Conveying Meaning: Professional Excellence
- Psychological Principles for Enhanced Meaning Conveyance
- Technology Tools and Platforms for Enhanced Meaning Conveyance
-
FAQ: Mastering the Art of Conveying Meaning
- What are the most effective techniques for conveying complex ideas simply?
- How can non-verbal communication enhance meaning conveyance in digital environments?
- What cultural factors should be considered when conveying meaning across international audiences?
- How do you measure the effectiveness of meaning conveyance in professional settings?
- What role does emotional intelligence play in conveying meaning effectively?
- How can storytelling techniques improve meaning conveyance in business communication?
- Future Trends in Conveying Meaning: Emerging Communication Paradigms
- Conclusion: Mastering the Continuous Evolution of Conveying Meaning
The Fundamental Science of Conveying Meaning: Cognitive and Linguistic Foundations
Conveying meaning operates on multiple cognitive and linguistic levels, involving complex neurological processes that transform abstract thoughts into communicable messages. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for anyone seeking to master effective communication.
Cognitive Processing in Meaning Creation
The process of conveying meaning begins in the cognitive realm, where thoughts, emotions, and intentions are formed:
Maybe you may be interestedThe Meaning of Cuddle in Hindi: Understanding the Language of AffectionMental Model Formation
- Conceptual frameworks: How our minds organize information into meaningful patterns
- Schema activation: Drawing upon existing knowledge structures to create new meaning
- Contextual processing: Integrating situational factors that influence message interpretation
- Intention formation: Developing clear communicative goals before message creation
- Audience modeling: Anticipating how recipients will process and interpret information
Encoding Processes
- Semantic encoding: Transforming abstract concepts into linguistic representations
- Syntactic structuring: Organizing ideas according to grammatical and logical patterns
- Pragmatic considerations: Adapting messages for specific communicative contexts
- Multi-modal integration: Combining verbal, visual, and gestural elements
- Cultural adaptation: Modifying messages for cross-cultural understanding
Linguistic Mechanisms for Meaning Transmission
The art of conveying meaning relies heavily on sophisticated linguistic tools and techniques:
Semantic Precision
- Denotative accuracy: Selecting words with precise literal meanings
- Connotative awareness: Understanding emotional and cultural associations
- Contextual appropriateness: Choosing language suitable for specific situations
- Register consistency: Maintaining appropriate formality levels
- Ambiguity avoidance: Eliminating potential sources of confusion
Rhetorical Strategies
- Aristotelian appeals: Utilizing ethos, pathos, and logos for persuasive communication
- Narrative structures: Organizing information in compelling story formats
- Metaphorical thinking: Using analogies and comparisons for complex concept explanation
- Repetition patterns: Reinforcing key messages through strategic reiteration
- Contrast techniques: Highlighting important points through juxtaposition
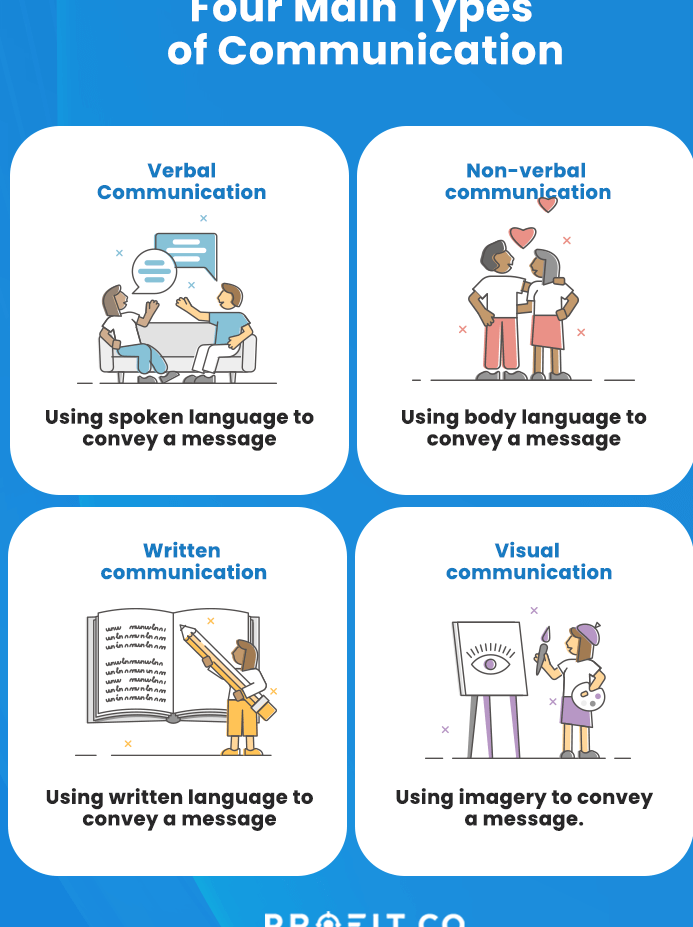
Multi-Modal Approaches to Conveying Meaning: Beyond Verbal Communication
Modern communication strategies for conveying meaning extend far beyond traditional verbal and written methods, incorporating sophisticated multi-modal approaches that engage multiple senses and cognitive processes simultaneously.
Maybe you may be interestedThe Delighted Meaning: Unraveling the True Essence of JoyVisual Communication and Symbolic Systems
Visual elements play an increasingly crucial role in conveying meaning across diverse contexts:
Typography and Textual Design
- Font psychology: How typeface choices influence message perception and credibility
- Hierarchy creation: Using size, weight, and spacing to guide attention and comprehension
- Color semantics: Leveraging color associations for emotional and cultural meaning
- Layout composition: Organizing visual elements to support message flow and understanding
- Readability optimization: Ensuring accessibility across diverse audiences and contexts
Symbolic Communication Systems
- Universal symbols: Utilizing widely recognized icons for cross-cultural communication
- Cultural iconography: Understanding culture-specific symbolic meanings and applications
- Brand semiotics: Creating consistent visual identity systems that convey organizational values
- Infographic design: Combining data visualization with narrative elements
- Emoji linguistics: Understanding the evolving language of digital pictographic communication
Non-Verbal Communication Mastery
The science of conveying meaning through non-verbal channels often communicates more powerfully than words alone:
Maybe you may be interestedYou Are My Crush: Unveiling the Meaning in TamilBody Language and Proxemics
- Posture psychology: How physical stance affects message credibility and reception
- Gesture semiotics: Understanding the communicative power of hand movements and facial expressions
- Spatial dynamics: Utilizing physical space to reinforce hierarchical and relational messages
- Eye contact patterns: Building trust and engagement through strategic visual connection
- Micro-expression awareness: Recognizing and managing involuntary facial communications
Vocal Communication Beyond Words
- Prosodic elements: Using rhythm, stress, and intonation for enhanced meaning
- Pace modulation: Controlling speaking speed for emphasis and comprehension
- Volume dynamics: Strategic use of loudness for attention and emotion
- Tonal variation: Conveying attitude and emotion through pitch changes
- Silence utilization: Understanding the communicative power of pauses and gaps
Digital Age Strategies for Conveying Meaning: Technology-Enhanced Communication
The digital revolution has fundamentally transformed how we approach conveying meaning, creating new opportunities and challenges for effective communication across virtual platforms and global audiences.
Platform-Specific Communication Optimization
Each digital platform requires unique strategies for effective meaning conveyance:
Maybe you may be interestedDecoding the Spam Meaning in Marathi: Unveiling its Cultural ContextSocial Media Communication
- Character limit mastery: Conveying complex messages within platform constraints
- Hashtag semantics: Using tags for discoverability and community engagement
- Visual storytelling: Combining images, videos, and text for enhanced impact
- Engagement algorithms: Understanding how platform mechanics affect message reach
- Cross-platform consistency: Maintaining coherent messaging across multiple channels
Professional Digital Communication
- Email effectiveness: Structuring professional messages for clarity and action
- Video conferencing presence: Optimizing virtual communication for maximum impact
- Presentation design: Creating compelling slide narratives that support verbal delivery
- Document formatting: Using visual hierarchy and structure for enhanced comprehension
- Digital collaboration: Facilitating meaningful exchanges in virtual team environments
Emerging Technologies and Communication Evolution
Cutting-edge technologies are creating new frontiers for conveying meaning:
Artificial Intelligence and Communication
- Natural language processing: Understanding how AI interprets and generates human communication
- Chatbot interaction design: Creating conversational interfaces that convey meaning effectively
- Personalization algorithms: Tailoring messages for individual audience preferences
- Sentiment analysis: Using AI to understand emotional undertones in communication
- Translation technology: Preserving meaning across language barriers through advanced software
Virtual and Augmented Reality Communication
- Immersive storytelling: Using 3D environments to enhance narrative impact
- Spatial audio design: Incorporating directional sound for enhanced meaning
- Haptic feedback: Adding tactile elements to digital communication
- Avatar psychology: Understanding how virtual representations affect message perception
- Environmental symbolism: Using virtual spaces as communicative tools
Cross-Cultural Mastery in Conveying Meaning: Global Communication Excellence
In our interconnected world, conveying meaning effectively across cultural boundaries has become essential for personal and professional success, requiring deep understanding of diverse communication styles and cultural contexts.
Maybe you may be interestedUnveiling the Intricacies of 'Neither Nor' Meaning in HindiCultural Communication Frameworks
Understanding cultural variations in communication patterns is crucial for effective meaning conveyance:
High-Context vs. Low-Context Cultures
- Contextual dependency: Understanding how much meaning is embedded in situational factors
- Implicit communication: Recognizing when meaning is conveyed through subtext and implication
- Explicit messaging: Adapting to cultures that prefer direct, detailed communication
- Relationship importance: Understanding how personal connections affect message interpretation
- Time orientation: Adapting communication styles for different temporal perspectives
Power Distance and Communication Hierarchy
- Authority recognition: Understanding how cultural power structures affect communication
- Formal vs. informal registers: Adapting language formality for cultural appropriateness
- Upward communication: Navigating hierarchical communication in high power distance cultures
- Egalitarian approaches: Adapting to cultures with flatter communication structures
- Age and experience respect: Incorporating cultural values into communication strategies
Language and Linguistic Adaptation
Effective cross-cultural meaning conveyance requires sophisticated understanding of linguistic variation:
Translation and Localization
- Semantic equivalence: Ensuring meaning preservation across languages
- Cultural adaptation: Modifying content for local cultural relevance
- Idiomatic expression: Understanding culture-specific figurative language
- Technical terminology: Adapting specialized vocabulary for different markets
- Legal and regulatory compliance: Ensuring translated content meets local requirements
Non-Native Speaker Communication
- Clarity prioritization: Simplifying complex concepts without losing meaning
- Cultural bridge-building: Using shared references and universal concepts
- Visual support integration: Supplementing verbal communication with visual aids
- Patience and repetition: Allowing time for processing and comprehension
- Feedback encouragement: Creating safe spaces for clarification requests
Industry-Specific Applications of Conveying Meaning: Professional Excellence
Different professional contexts require specialized approaches to conveying meaning, each with unique challenges, audiences, and success metrics.
Business and Corporate Communication
Professional meaning conveyance in business contexts requires understanding of organizational dynamics and stakeholder needs:
Executive Communication
- Strategic messaging: Aligning communication with organizational vision and goals
- Stakeholder management: Tailoring messages for different audience interests and concerns
- Crisis communication: Maintaining clarity and confidence during challenging situations
- Change management: Conveying transformation initiatives in ways that inspire and motivate
- Performance communication: Delivering feedback and expectations with clarity and support
Marketing and Brand Communication
- Brand narrative development: Creating consistent stories that resonate with target audiences
- Emotional connection: Using psychological triggers to create meaningful brand relationships
- Value proposition clarity: Articulating unique benefits in compelling, understandable terms
- Customer journey mapping: Ensuring consistent messaging across all touchpoints
- Conversion optimization: Using persuasive communication to drive desired actions
Educational and Training Contexts
Educational communication for conveying meaning requires understanding of learning processes and diverse student needs:
Pedagogical Communication Strategies
- Learning style adaptation: Presenting information in multiple formats for diverse learners
- Scaffolding techniques: Building complex understanding through progressive concept development
- Assessment communication: Providing feedback that promotes growth and understanding
- Inclusive communication: Ensuring all students can access and understand content
- Motivation and engagement: Using communication techniques that inspire learning
Professional Development Communication
- Skill transfer facilitation: Helping learners apply new knowledge in practical contexts
- Adult learning principles: Respecting experience while introducing new concepts
- Performance improvement: Communicating expectations and support for professional growth
- Knowledge retention: Using repetition and reinforcement for lasting learning
- Evaluation and reflection: Encouraging self-assessment and continuous improvement
Psychological Principles for Enhanced Meaning Conveyance
Understanding the psychological mechanisms underlying effective communication enables more sophisticated and impactful approaches to conveying meaning across diverse contexts and audiences.
Cognitive Load Management
Cognitive psychology provides crucial insights for optimizing how audiences process and retain communicated meaning:
Information Processing Optimization
- Chunking strategies: Breaking complex information into manageable, memorable segments
- Working memory considerations: Respecting cognitive limitations in message design
- Attention management: Using focus techniques to highlight essential information
- Redundancy reduction: Eliminating unnecessary information that creates cognitive burden
- Sequential organization: Presenting information in logical, progressive order
Memory Enhancement Techniques
- Encoding specificity: Creating memorable contexts that aid recall
- Elaborative processing: Encouraging deeper thinking about communicated concepts
- Visual-verbal integration: Combining multiple sensory channels for enhanced retention
- Spaced repetition: Timing message reinforcement for optimal memory consolidation
- Emotional anchoring: Using emotional connections to strengthen memory formation
Persuasion and Influence Psychology
The science of persuasion offers powerful tools for conveying meaning in ways that inspire action and change:
Cialdini's Principles of Influence
- Reciprocity utilization: Creating obligations through valuable communication
- Commitment consistency: Aligning messages with audience values and prior commitments
- Social proof integration: Using community validation to strengthen message credibility
- Authority establishment: Building credibility through expertise demonstration
- Liking enhancement: Creating personal connections that facilitate message acceptance
- Scarcity communication: Highlighting unique value and limited opportunities
Emotional Intelligence in Communication
- Emotional awareness: Recognizing and managing personal emotional states during communication
- Empathy application: Understanding and responding to audience emotional needs
- Social skill utilization: Managing relationships through effective communication
- Motivation alignment: Connecting messages with audience intrinsic motivations
- Self-regulation demonstration: Modeling emotional control and professional communication
Technology Tools and Platforms for Enhanced Meaning Conveyance
Modern communication technology provides unprecedented opportunities for conveying meaning more effectively, efficiently, and engagingly than ever before.
Design and Visual Communication Tools
Digital design platforms enable sophisticated visual meaning conveyance:
Professional Design Software
- Adobe Creative Suite: Professional-grade tools for complex visual communication projects
- Canva and accessible design: User-friendly platforms for quick, effective visual creation
- Figma collaboration: Team-based design tools for iterative meaning development
- Sketch and prototyping: Interface design tools for digital communication experiences
- Presentation software: PowerPoint, Keynote, and Prezi for structured information delivery
Data Visualization and Infographics
- Tableau and data storytelling: Transforming complex data into understandable narratives
- D3.js custom visualizations: Creating unique, interactive data communication experiences
- Infogram and timeline tools: Specialized platforms for specific visualization needs
- Mind mapping software: Visual organization tools for complex concept relationships
- Chart and graph optimization: Best practices for statistical communication
Collaborative Communication Platforms
Team communication tools enable more effective collective meaning creation and sharing:
Real-Time Collaboration
- Slack and team messaging: Organized conversation spaces for different topics and projects
- Microsoft Teams integration: Combining communication with productivity tools
- Zoom and video communication: Face-to-face interaction for enhanced meaning conveyance
- Google Workspace collaboration: Real-time document and project collaboration
- Project management communication: Integrating communication with task and timeline management
Content Management and Distribution
- Content management systems: Organizing and distributing information efficiently
- Social media management: Coordinating multi-platform communication strategies
- Email automation: Personalizing mass communication for individual relevance
- Video hosting and streaming: Distributing visual content for maximum reach and impact
- Podcast and audio platforms: Utilizing voice communication for intimate, personal connection
FAQ: Mastering the Art of Conveying Meaning
What are the most effective techniques for conveying complex ideas simply?
The most effective techniques for conveying complex ideas include analogical thinking (using familiar comparisons), progressive disclosure (revealing information in logical steps), visual scaffolding (supporting explanations with diagrams and examples), narrative structuring (embedding concepts in relatable stories), and chunking strategies (breaking large concepts into manageable components). Additionally, using multiple representation modes—combining verbal explanations with visual aids, examples, and interactive elements—helps accommodate different learning styles and reinforces understanding through multiple cognitive pathways.
How can non-verbal communication enhance meaning conveyance in digital environments?
In digital environments, non-verbal communication for enhanced meaning conveyance includes strategic use of visual design elements (typography, color, layout), video communication optimization (camera positioning, lighting, background choices), emoji and symbolic communication (adding emotional context to text), timing and pacing (strategic use of delays and real-time responses), and interactive design elements (buttons, animations, and user interface cues that guide attention and action). These techniques compensate for the loss of physical presence while creating new opportunities for meaning enhancement through deliberate digital design choices.
What cultural factors should be considered when conveying meaning across international audiences?
Cultural factors for international meaning conveyance include high-context vs. low-context communication preferences (implicit vs. explicit messaging), power distance considerations (hierarchical vs. egalitarian communication styles), individualistic vs. collectivistic values (personal achievement vs. group harmony emphasis), temporal orientation differences (linear vs. circular time concepts), religious and philosophical frameworks (underlying worldview assumptions), color and symbol associations (culture-specific meanings), and gender role expectations (communication style variations). Successful international communication requires research, cultural sensitivity, local partnerships, and iterative testing with target audiences.
How do you measure the effectiveness of meaning conveyance in professional settings?
Measuring effectiveness of meaning conveyance in professional settings involves comprehension assessment (testing audience understanding through questions and feedback), behavioral change tracking (observing whether communication leads to desired actions), engagement metrics analysis (measuring attention, participation, and retention), feedback loop establishment (creating systems for ongoing communication evaluation), objective achievement measurement (assessing whether communication goals are met), and long-term impact evaluation (tracking sustained understanding and application over time). Professional communication effectiveness should be measured through both quantitative metrics and qualitative feedback.
What role does emotional intelligence play in conveying meaning effectively?
Emotional intelligence in meaning conveyance involves self-awareness of communication style (understanding personal communication strengths and biases), empathy application (anticipating audience emotional responses and needs), emotional regulation (managing personal emotions to maintain clear communication), social awareness (reading group dynamics and individual responses), and relationship management (adapting communication style for different individuals and situations). High emotional intelligence enables communicators to create psychological safety, build trust, navigate conflicts constructively, and ensure that emotional undertones support rather than undermine intended meaning.
How can storytelling techniques improve meaning conveyance in business communication?
Storytelling techniques for business communication include narrative arc development (creating compelling beginnings, conflicts, and resolutions), character identification (helping audiences connect with relatable protagonists), concrete detail integration (using specific examples rather than abstract concepts), emotional engagement (incorporating feelings and personal stakes), metaphor and analogy use (making complex business concepts accessible), and visual storytelling elements (combining narrative with supporting visual materials). Stories make business communication more memorable, persuasive, and emotionally engaging while helping audiences understand complex information through familiar narrative structures.
Future Trends in Conveying Meaning: Emerging Communication Paradigms
The landscape of conveying meaning continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing social dynamics, and new understanding of human psychology and communication effectiveness.
Artificial Intelligence and Communication Enhancement
AI-powered communication tools are revolutionizing how we approach meaning conveyance:
Personalization and Adaptation
- Dynamic content optimization: AI systems that adapt messages in real-time based on audience response
- Personality-based communication: Tailoring message style and content for individual psychological profiles
- Cultural intelligence automation: AI tools that automatically adapt content for different cultural contexts
- Learning preference recognition: Systems that identify and accommodate individual learning and communication styles
- Emotional state detection: Technology that recognizes and responds to audience emotional needs
Enhanced Translation and Interpretation
- Real-time meaning preservation: Advanced translation that maintains cultural and emotional nuance
- Context-aware interpretation: AI that understands situational factors affecting meaning
- Visual communication translation: Technology that adapts images and symbols for different cultures
- Multimodal translation: Comprehensive conversion between different communication modes
- Collaborative human-AI communication: Partnerships between human insight and AI processing power
Immersive and Interactive Communication Technologies
Next-generation communication platforms are creating unprecedented opportunities for meaning conveyance:
Virtual and Augmented Reality Applications
- Experiential communication: Creating shared virtual experiences for enhanced understanding
- Spatial information design: Using 3D environments to organize and present complex information
- Haptic meaning conveyance: Adding touch and physical sensation to communication
- Presence enhancement: Creating stronger emotional connections through immersive technology
- Collaborative virtual spaces: Enabling team communication in shared digital environments
Conclusion: Mastering the Continuous Evolution of Conveying Meaning
The art and science of conveying meaning represents one of humanity's most sophisticated and essential capabilities, encompassing cognitive psychology, linguistic precision, cultural awareness, technological fluency, and emotional intelligence. As our communication landscape continues to evolve rapidly, the ability to adapt and master new methods of meaning conveyance becomes increasingly crucial for personal success, professional advancement, and meaningful human connection.
From the foundational cognitive processes that transform abstract thoughts into communicable messages, to the cutting-edge AI technologies that personalize and optimize our communication efforts, effective meaning conveyance requires continuous learning, practice, and adaptation. The integration of traditional communication wisdom with modern technological capabilities creates unprecedented opportunities for clarity, impact, and connection across diverse audiences and contexts.
The future of conveying meaning lies not in choosing between human insight and technological enhancement, but in skillfully combining both to create communication experiences that are more personalized, culturally sensitive, emotionally intelligent, and ultimately more effective at achieving our deepest communication goals—understanding, connection, and positive change.
As we continue to navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world, the mastery of conveying meaning remains our most powerful tool for building bridges across differences, inspiring action toward shared goals, and creating the mutual understanding essential for human flourishing and collaboration.
The journey of mastering conveying meaning is lifelong, requiring continuous attention to emerging technologies, evolving cultural dynamics, and deeper understanding of human psychology—but the rewards of clear, impactful communication make this ongoing development one of the most valuable investments we can make in our personal and professional lives.
Si quieres conocer otros artículos parecidos a Conveying Meaning: The Art of Effective Communication puedes visitar la categoría SOCIETY.




